Phencyclidine Screening Test
The QuickScreen™ One Step Phencyclidine Screening Test is a rapid, qualitative immunoassay for the detection of Phencyclidine in urine. The cutoff concentration for this test is 25 ng/mL, as recommended by the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (SAMHSA), formerly the U.S. National Institute of Drug Abuse (NIDA). This test provides only a preliminary test result. A more specific alternate testing method must be used in order to obtain a confirmed analytical result. Gas chromatography/mass spectrometry (GC/MS) is the preferred confirmatory method. Other chemical confirmation methods are available. Clinical consideration and professional judgment should be applied to any drug of abuse test result, particularly when preliminary positive results are observed.
Phencyclidine, commonly known as PCP or angel dust is used primarily as a recreational drug for its hallucinogenic effects. PCP is commonly taken orally, by inhalation, by insufflation or intravenously. It is well absorbed following all routes of administration, concentrating fastest in fatty tissues and the brain. Unchanged PCP is excreted in the urine in moderate amounts (10% of the dose). The terminal half-life for PCP varies considerably, with a range of 8 – 55 hours, averaging of 18 hours. The effects of PCP are unpredictable and variable. Depending on the amount used, the user may show signs of euphoria, relaxation, increased strength, time and space distortions, anxiety, panic, and hallucination. Urine based screening tests for drugs of abuse range from complex analytical procedures to simple immunoassay tests. The sensitivity and rapidity of the immunoassays have made them the most accepted method of preliminary screening for drugs of abuse in urine. This allows the laboratory to eliminate the large number of negative specimens and focus on the smaller number of initially positive specimens.
The QuickScreen™ One Step Phencyclidine Test is a competitive immunoassay that is used to screen for the presence of Phencyclidine in urine. It is a chromatographic absorbent device in which drugs or drug metabolites in a sample compete with drug / protein conjugate immobilized on a porous membrane for a limited number of antibody /dye conjugate binding sites. The test device employs a unique combination of monoclonal and polyclonal antibodies to selectively identify Phencyclidine in urine with a high degree of confidence. In the assay procedure, a urine sample is added to the test device in the Sample Well, where it is absorbed into the device by capillary action. The urine mixes with the antibody-dye conjugate and flows across the pre-coated membrane. When sample PCP levels are below 25 ng/mL (the detection sensitivity of the test), antibody / dye conjugate binds to the drug / protein conjugate immobilized in the Test Region (T) of the device. This produces a colored Test Band that, regardless of its intensity, indicates a negative result. When sample PCP levels are at or above 25 ng/mL, the free drug in the sample binds to the antibody / dye conjugate, preventing the antibody / dye conjugate from binding to the drug / protein conjugate immobilized in the Test Region (T) of the device. This prevents the development of a distinct colored band, indicating a potentially positive sample. In either case, a colored Control Band is produced in the Control Region (C) by a non-specific antibody-dye / conjugate reaction. This band serves as a built-in quality control device that demonstrates antibody recognition and reactivity as well as confirmation that the test is complete.
-

Amphetamine
$2.80Drug Screen
-
No
IVD
Qualitative
Urine
RAP-2834
$2.8
-

Amphetamine (7mm cassette)
$3.00Drug Screen
No
IVD
Qualitative
Urine
RAP-2835
$3
-

Amphetamine Test Strip
$1.80Drug Screen
-
No
IVD
-
Urine
RAP-3306
$1.8
-

Cocaine
$3.00Drug Screen
No
IVD
Qualitative
Urine
RAP-2839
$3
Call Us Now! A Representative Is Standing By To Help.
Testosterone Administration During Energy Deficit Suppresses Hepcidin and Increases Iron Availability for Erythropoiesis
Testosterone Administration During Energy Deficit Suppresses Hepcidin and Increases Iron Availability for Erythropoiesis Context: Severe energy deprivation markedly inhibits erythropoiesis by restricting iron availability for hemoglobin synthesis. Objective:...
Role of Hepcidin to Identify the Type of Anemia in Chronic Kidney Disease in Children
Role of Hepcidin to Identify the Type of Anemia in Chronic Kidney Disease in Children See full study: https://iopscience.iop.org/article/10.1088/1742-6596/1246/1/012023/meta Abstract Chronic kidney disease (CKD) may present with anemia of chronic disease (ACD),...
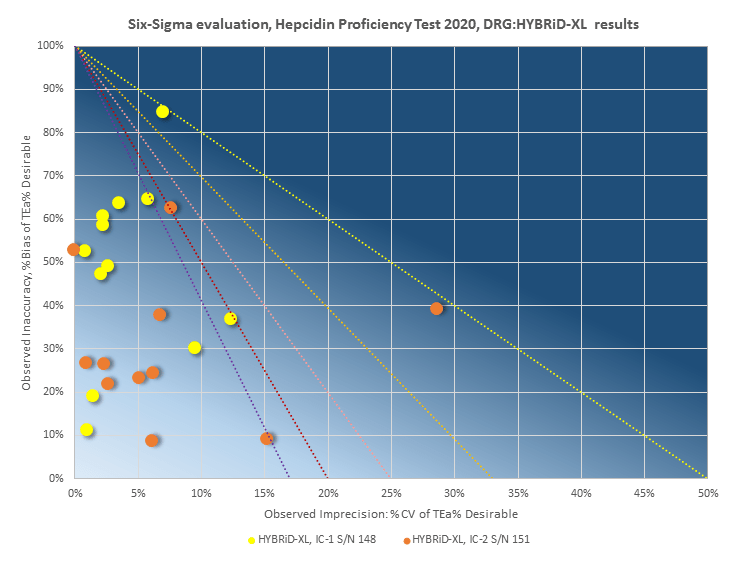
Hepcidin 25 Proficiency Test
On April 30th, 2020, an organized study by Radboud University Medical Center in Nijmegen, Netherlands, has completed a final report for the DRG International’s first ever Hepcidin Proficiency Test.
Click the link to learn more about how DRG is certified in the manufacturing and distribution of in-vitro diagnostic reagents used in the diagnosis of autoimmune status, cancer, cardiac markers, disease status, fertility testing, pregnancy testing, diabetes and immune status.

Click the link to learn more about how DRG is certified in the manufacturing and distribution of in-vitro diagnostic reagents used in the diagnosis of autoimmune status, cancer, cardiac markers, disease status, fertility testing, pregnancy testing, diabetes and immune status.

